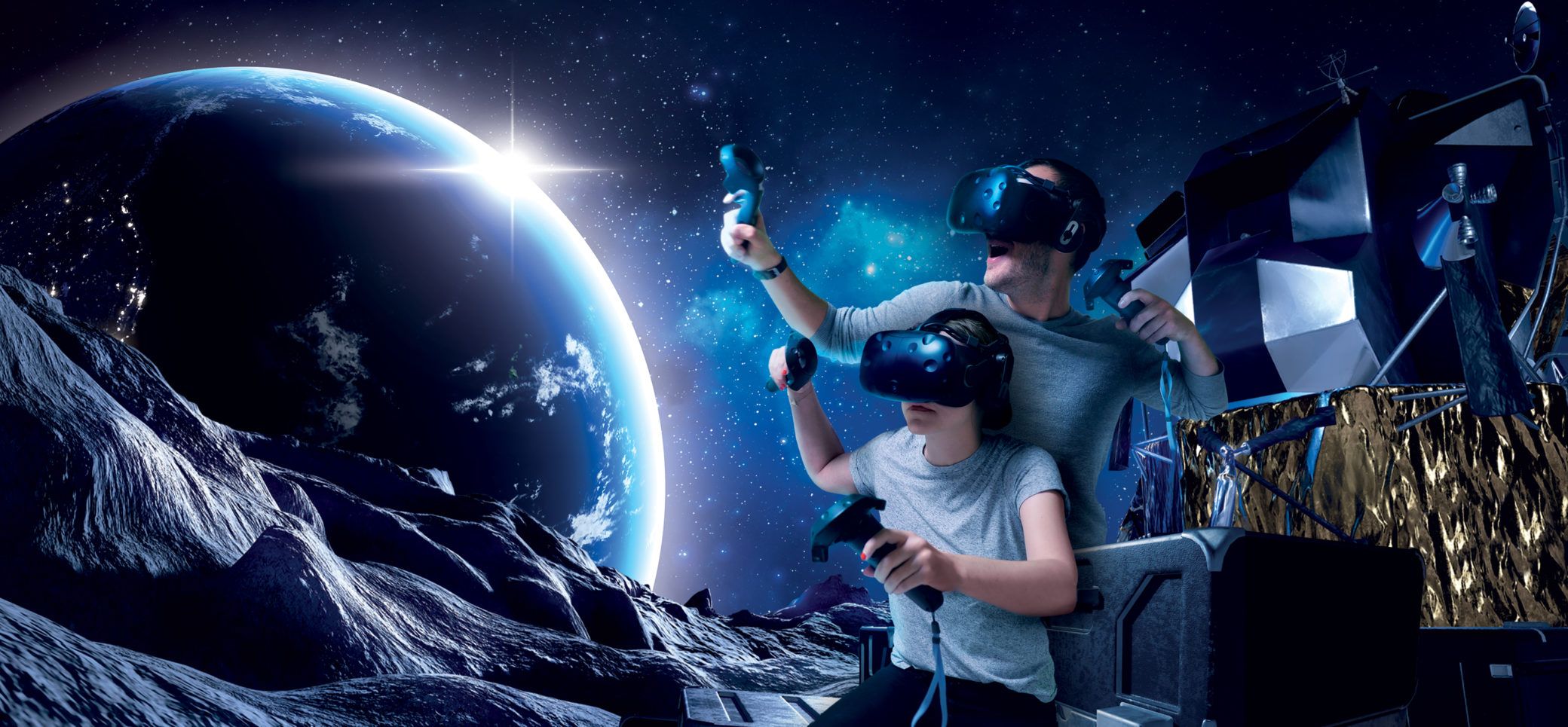
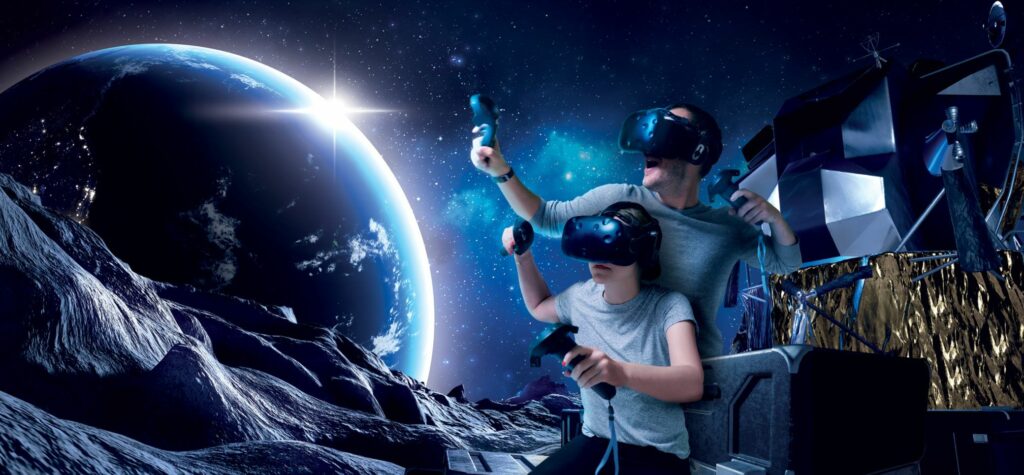
Imagine sitting in a compact cockpit, hands gripping a smooth joystick. Outside the window, fluffy white clouds drift past, and the distant hum of jet engines fills your ears. You tilt the joystick slightly to the left, and the horizon shifts — your body even leans instinctively, as if you’re truly thousands of feet in the air. But here’s the twist: you’re not in a real plane. You’re in a small room, wearing a sleek headset, and every sight, sound, and subtle vibration is generated by a machine.
This mind-bending blend of “real”sensation and virtual space is the magic of a virtual reality (VR) simulator. It’s far more than just strapping on a headset — it’s a carefully engineered system that tricks your brain into believing you’re somewhere else. So, What exactly Is a Virtual Reality Simulator, and how does it work? Let’s dive in.

First Things First: What Is a Virtual Reality Simulator?
At its core, a vr simulator is a technology system that uses computer software and specialized hardware to create a highly realistic, interactive 3D virtual environment — then simulates how a user would sense and interact with that environment.
To break down its key components:
- Virtual Environment: A digital world built by computers, whether it’s a flight path, a surgical operating room, or a fantasy landscape.
- Interactivity: Unlike a pre-recorded video, users can change the environment—e.g., moving a virtual tool, steering a plane, or opening a door.
- Multi-Sensory Immersion: The goal isn’t just to “show” you a virtual world, but to fool your senses (sight, sound, touch, even balance) into thinking you’re there.
Virtual Reality Simulator vs. Virtual Reality Headset: Don’t Mix Them Up
A common misconception is equating a VR simulator with a VR headset (like the Meta Quest 3 or HTC Vive Pro 2). But they’re not the same—think of a headset as a “window,” while a simulator is the entire house it looks into.
VR Headset
What It Is: A single hardware device that displays 3D visuals to your eyes. It’s the “display” for virtual content.
Key Example: Meta Quest 3, PlayStation VR2
VR Simulator
What It Is: A complete system that combines hardware, software, and computing power to create a fully immersive experience.
Key Example: A vr flying simulator (headset + joystick + vibration seat + flight software) or a vr racing simulator (VR glasses + force feedback steering wheel + real accelerator pedal + blowing effect + dynamic platform)
In short: A headset is part of a simulator, but a simulator needs far more to deliver true immersion.
What Are The Three Types of Virtual Reality Simulator: From “Basic” to “Full Immersion”
Not all virtual reality simulators feel the same. They’re grouped by how “immersed” they make you feel—from casual screen-based interactions to full sensory surroundings.
1. Non-Immersive VR (The “Entry Level”)
This is the most common and affordable type. You interact with a virtual environment through a standard computer screen, keyboard, or mouse—you never lose sight of the real world around you.
- How it feels: Like playing a detailed video game, but with virtual 3D elements.
- Key examples: Microsoft Flight Simulator (played on a PC monitor with a mouse/joystick) or The Sims 4 (building virtual homes on a laptop).
- Best for: Casual users, beginners, or scenarios where full immersion isn’t needed.
Is VR Gaming a Good Business?
Yes, VR games are not just about the VR arcade profit; they are about the the gamers’ interests. The allure of virtual reality transports gamers to new dimensions of excitement and thrill. Then the demand for innovative gaming solutions continues to rise, driven by a community that craves interactive storytelling and engaging challenges.
It Boasts Various Types and Styles of VR Simulator Machines.
VR gaming’s appeal is further enhanced by the variety of VR machines for sale and styles that cater to different gamer preferences.
Room-Scale VR Systems
These setups, like the VR Doomsday Cage Simulator and VR Space Ride Simulator, allow players to physically move within a designated area, offering a highly immersive experience. Room-scale VR is popular for adventure and puzzle games, where movement and interaction are crucial.
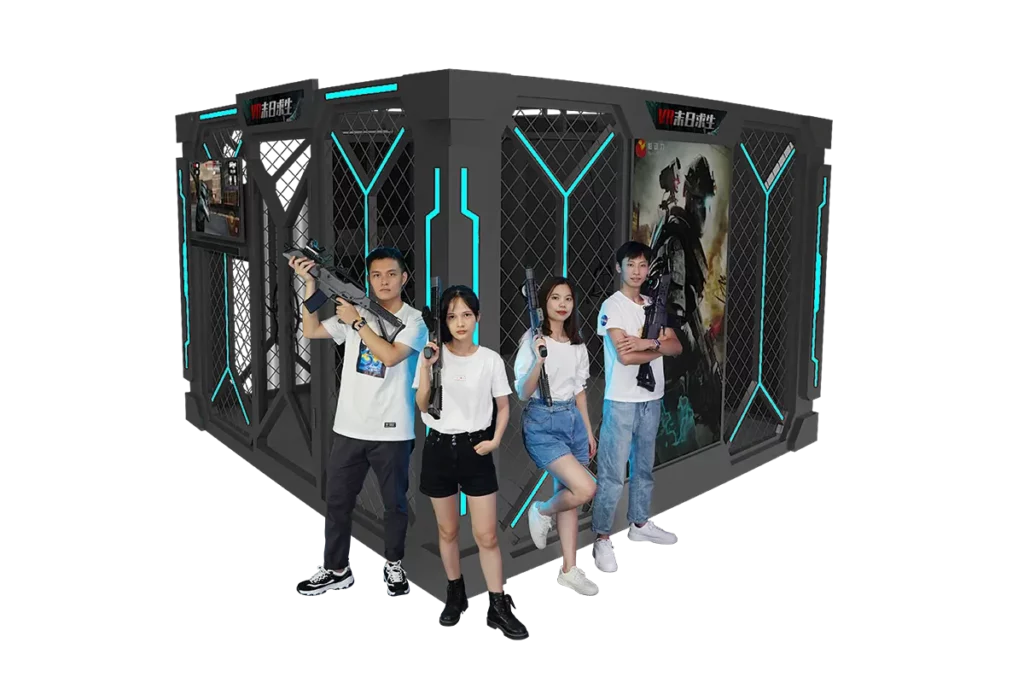


Cockpit Simulators
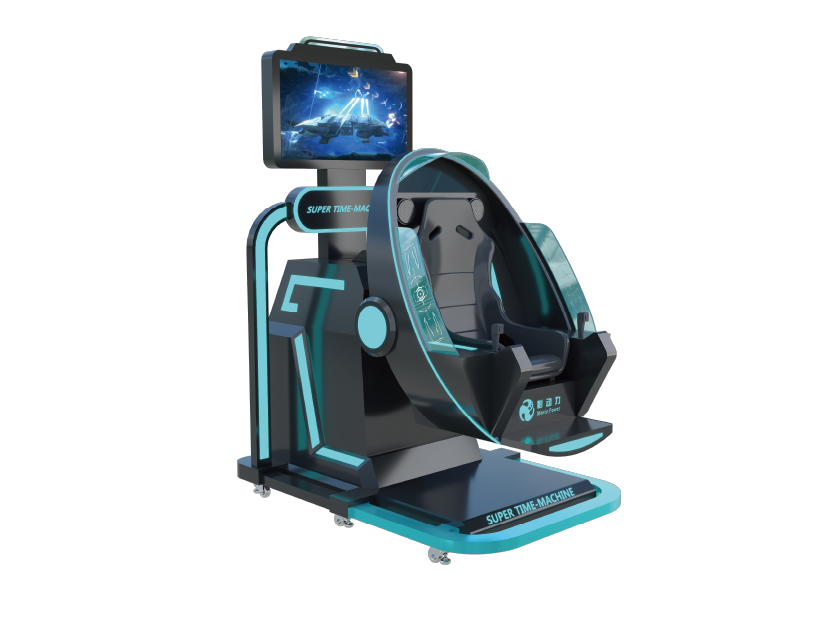
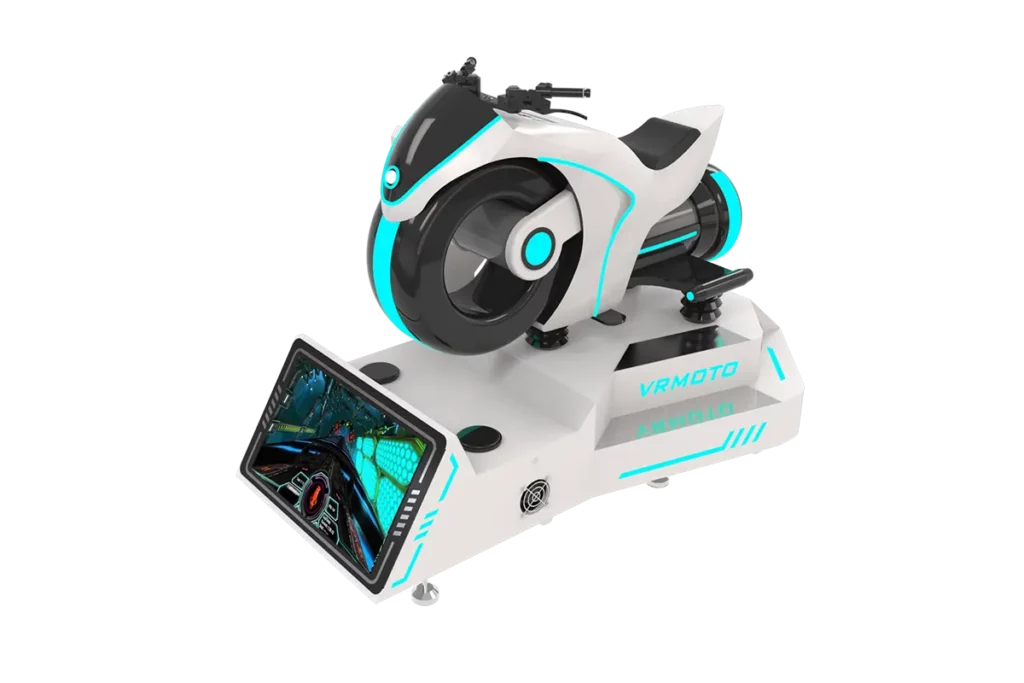
These machines are designed for racing or flight simulation games. Examples include the VR Super 360 Flight Simulator and VR Motorcycle Simulator, which provide realistic seating and controls, creating an authentic simulation experience.


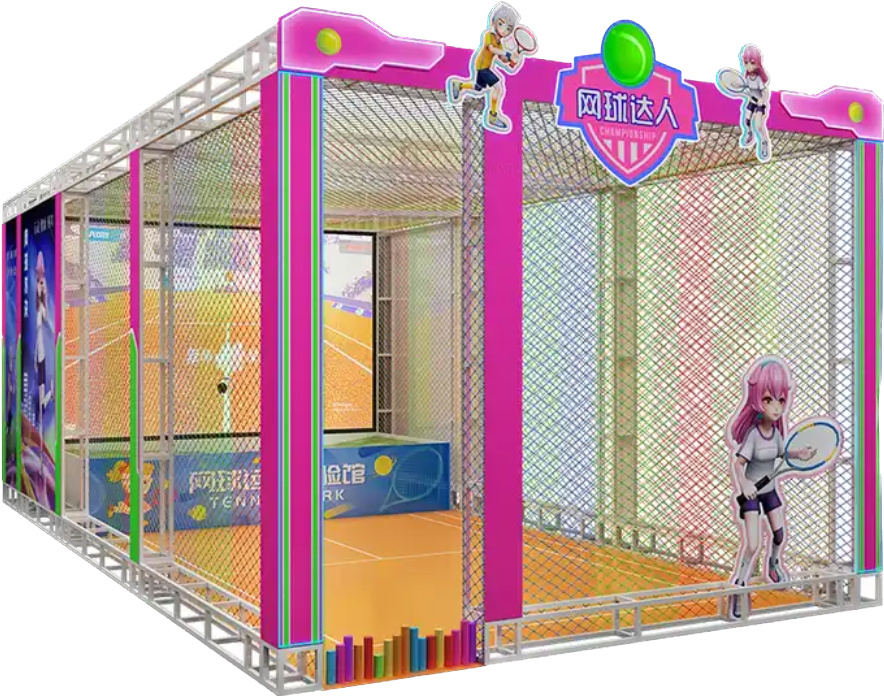
Omnidirectional Treadmills
Devices like the Virtuix Omni and VR Tennis Simulator let players walk or run in any direction within a game, enhancing the sense of immersion. These treadmills are popular in first-person shooters and adventure games.

Haptic Feedback Suits
Companies like Teslasuit and bHaptics offer suits and vests that provide tactile feedback, allowing players to feel in-game actions. Besides, some VR game simulators will provide VR headsets, consoles, or VR machine equipment to achieve this physical interaction. VR X-spy Simulator with a VR gun is not an exception. This technology is particularly appealing for action and combat games, where physical sensations add to the realism.
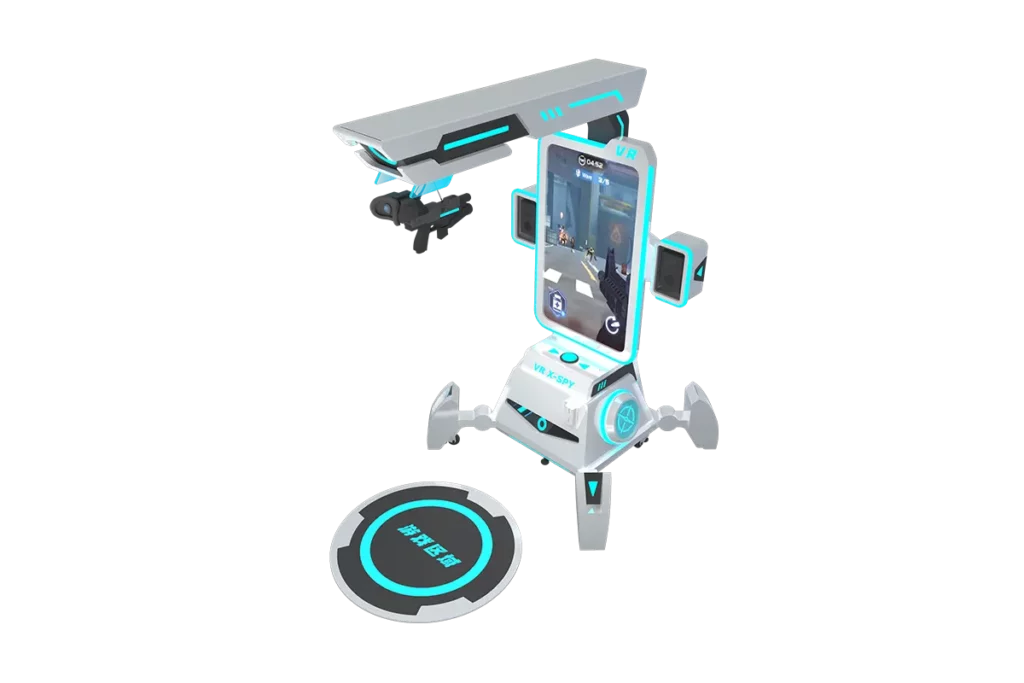
It Meets the Gamer’s Interests.
Here are two cases that attract amounts of gamers through innovative storytelling and VR plays.
Case 1: Zero Latency
Zero Latency, a pioneer in the VR gaming space, has demonstrated the profitability and popularity of VR gaming businesses. Founded in 2013, Zero Latency has expanded to over 45 locations worldwide. Their free-roam VR experiences allow players to move untethered in a large space, providing an immersive and interactive gaming environment. This innovative approach has attracted a broad audience, from casual gamers to VR enthusiasts, ensuring consistent revenue and growth.
Case 2: The VOID
The VOID, another successful VR gaming company, offers hyper-reality experiences that combine physical environments with VR simulations. The VOID has partnered with major franchises like Star Wars and Marvel to create unique, story-driven experiences that attract large crowds. Their innovative approach to blending physical and virtual worlds has set a new standard in the industry, demonstrating the high demand and profitability of VR gaming.
It Has Specific Business Models.
VR gaming businesses can adopt various business models to maximize profitability:
- Subscription Services: A subscription-based model allows customers to pay a monthly or yearly fee for unlimited access to a library of VR games and experiences. This model ensures a steady revenue stream and fosters customer loyalty. For example, VR World NYC provides membership plans that offer regular users unlimited access, enhancing customer retention and satisfaction.
- Pay-to-Play Models: This traditional arcade-style model charges players per session or game. It’s suitable for locations with high foot traffic, where customers will likely pay for short-term, intense gaming experiences. Sandbox VR effectively utilizes this model by charging per session, attracting groups for one-time immersive experiences.
- Event Hosting and Rentals: Renting out VR equipment for events such as parties, corporate gatherings, or trade shows can be a lucrative revenue stream. Companies like The VR Company offer comprehensive event packages, including setup, staff assistance, and a curated selection of VR experiences.
- Branded Experiences and Sponsorships: Partnering with brands to create branded VR experiences or incorporating product placements within existing games can generate significant revenue. For example, Nike collaborated with VR developers to create immersive running experiences that promote their products while providing engaging content for users.
- Franchise Opportunities: Offering franchise opportunities allows entrepreneurs to leverage established VR gaming brands and business models while providing support and resources for setting up and running VR arcade locations. Ctrl V is a prime example of a successful VR arcade franchise, with locations across North America.
Is a VR Arcade Profitable?
Yes, a VR arcade can be highly profitable, thanks to the booming virtual reality industry and increasing consumer interest. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global location-based VR market, which includes VR arcades, is projected to grow from USD 1.2 billion in 2020 to USD 12.6 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.5%. This rapid growth indicates strong profitability potential for VR arcades.
Let’s overview two real-world cases in the VR arcade chain.
Case 1: VR World NYC
VR World NYC is a prime example of a successful VR arcade. Since its launch, VR World NYC has drawn in thousands of visitors monthly, achieving profitability within its first year. The arcade offers a diverse range of VR arcade games, from intense action experiences to creative and educational simulations. By catering to a broad audience, VR World NYC ensures steady revenue. Their strategic location and emphasis on a high-quality virtual reality game experience have been key to their success.
Case 2: Sandbox VR
Another successful example is Sandbox VR, which raised $11 million in funding in 2019 and has expanded to multiple locations globally. Sandbox VR focuses on delivering high-quality, immersive VR experiences using advanced vr arcade machines. Their commitment to offering unique and engaging experiences has led to high customer retention and repeat visits. Sandbox VR’s business model, which emphasizes customer service and innovative gameplay, highlights the profitability and potential of investing in a virtual reality game room.
Overall, these examples and market projections highlight that VR arcades can be highly profitable ventures, especially when strategically located and well-managed.
Is VR Growing or Dying? Learn by VR Machine Equipment
The market dynamics shaping the AR/VR industry are multifaceted, influenced by factors that propel technological progress and consumer engagement. While recent data indicated a decline in VR headset sales in the U.S., experts project a recovery in shipments as demand rebounds. Market drivers such as enhanced content offerings, improved user interfaces, and expanding application domains are instrumental in sustaining growth momentum within the virtual reality ecosystem.
As you can see, since the demand for immersive experiences continues to evolve, the market dynamics surrounding VR headset sales provide valuable insights into the industry’s growth or decline. Let’s delve into the sales figures and projections to gain a deeper understanding of VR’s current trajectory and prospects.
VR Headset Sales
Witness the surge in demand for Virtual Reality (VR) headsets, a testament to the evolving landscape of immersive technology. From 2019 to 2028, global sales volumes are forecasted to experience a remarkable growth trajectory. By the end of this decade, VR headset adoption is predicted to reach an impressive 24.7 million units, reflecting a substantial increase in consumer interest and market expansion.
AR Headset Sales
In contrast to VR headset sales, the augmented reality (AR) and VR device shipments faced a temporary setback in the first quarter of 2023. However, projections indicate a resurgence in 2024, with shipments expected to surge by 44.2% to reach 9.7 million units. This anticipated rebound underscores the resilience of the AR/VR market and signals a positive outlook for future industry growth.
Is There a Future for VR Gaming?
Yes, with technological advancements and increasing consumer interest, the future of VR gaming appears promising. Let’s explore the current adoption rates and future potential of VR gaming to gain insight into its trajectory and prospects.
Because It Features Technological Advancements.
The hardware and software developments herald a bright future for VR gaming, offering players increasingly immersive, interactive, and captivating experiences that push the boundaries of virtual reality technology.
Hardware Improvements
- Higher-Resolution Displays: Next-generation VR headsets boast sharper displays with higher pixel densities, resulting in clearer visuals and reduced screen-door effects.
- Lighter and More Comfortable Headsets: Manufacturers are prioritizing comfort by designing lighter headsets with better weight distribution and improved ergonomic features, allowing for longer gaming sessions without discomfort.
- Advanced Motion Tracking Sensors: Enhanced tracking technology enables more precise and responsive movement detection, providing a smoother and more immersive gaming experience.
- Wireless Connectivity: The shift towards wireless VR solutions reduces tethering restrictions, allowing for greater freedom of movement and eliminating cable clutter.
Software Developments
- Immersive Storytelling: Developers are crafting compelling narratives and immersive worlds that draw players into rich and engaging storytelling experiences, blurring the lines between reality and virtuality.
- Interactive Simulations: VR simulations are becoming more interactive and realistic, offering immersive training environments for industries like healthcare, education, and aviation.
- Multiplayer Environments: Multiplayer VR games and social experiences are on the rise, enabling players to interact and collaborate with others in virtual worlds, fostering a sense of community and camaraderie.
- Advancements in AI and Machine Learning: AI-driven NPCs (non-player characters) and dynamic environments enhance in-game interactions and adaptability, creating more lifelike and challenging gaming scenarios.
Because It Enjoys Consumer Adoption.
The future of VR gaming is promising, driven by increasing consumer adoption and a growing interest in immersive gaming experiences. Current adoption rates indicate a rising trend, with more players embracing VR technology for gaming and entertainment. According to a report by Statista, the number of active VR users worldwide is projected to reach 171 million by 2028, reflecting a significant increase from previous years.
Looking ahead, the potential for future adoption of VR gaming is substantial. As VR hardware becomes more affordable, accessible, and user-friendly, barriers to entry are gradually diminishing. Moreover, the continuous development of high-quality VR content and experiences is attracting a broader audience, including casual gamers, enthusiasts, and mainstream consumers.
Factors such as advancements in VR technology, expanding content libraries, and the integration of VR into other industries beyond gaming, such as education, healthcare, and virtual tourism, further contribute to the growing interest and adoption of VR gaming.
Make Great Profits by VR Arcade
In conclusion, starting a VR arcade is not only a viable business venture but also a potentially lucrative one. With increasing consumer interest in VR gaming and the growing market demand for immersive experiences, investing in a VR arcade is indeed a good investment. By capitalizing on this trend and providing unique and engaging VR experiences, entrepreneurs can tap into a profitable market while offering customers unforgettable entertainment. So why wait? Start a VR arcade today and embark on a journey towards great profits and success.



